A Recycled Car's Journey

For the one million cars that are scrapped in the UK each year, you might think it’s the end of the road. But with even the most unroadworthy of motors, the scrapyard is only the start of the journey.
With the average car comprising of 30,000 parts – and ‘sustainability’ being the latest buzzword – we examine those components and materials, and where else you’ll find them.
An electric car’s battery pack can be recycled into 125 metres of copper piping
Our use-again-and-again approach goes well beyond paper straws and bags for life. When it comes to cars, almost all of the materials can be repurposed elsewhere.
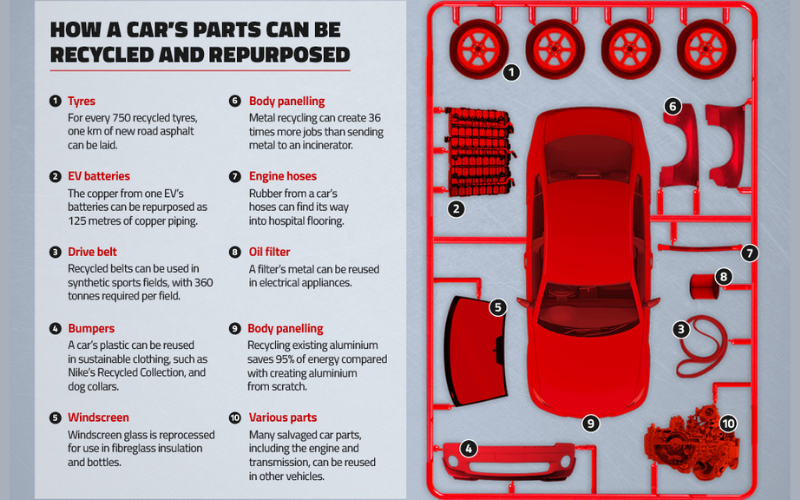
The rubber from tyres, drive belts and hoses, for example, can be used in synthetic sports fields, hospital flooring and even the laying of new road surfaces. Metals like copper can find their way into plumbing, roofing and coins, while reprocessing aluminium can save up to 95% of the energy required to produce it from scratch.
Car components themselves, made up of several materials, can also be used transferred to other vehicles, avoiding the need for new production.
UK scrapping salvages 30 billion parts every year
Scrapyards are often seen as car graveyards, but the reality is quite the opposite, as UK legislation ensures that a minimum 95% of a scrapped car is recycled. In all, UK car scrapping can retrieve as many as 30 billion parts a year from motors that are no longer roadworthy.
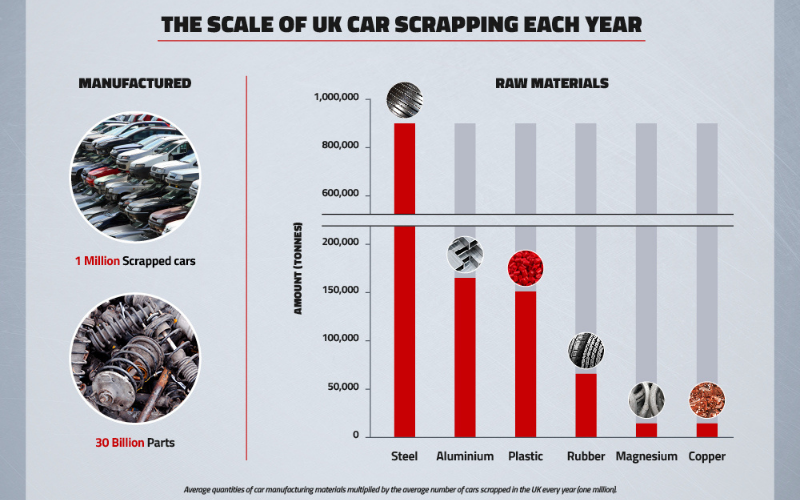
The most abundant resource is steel, with an estimated 900,000 tonnes retrieved annually. In second is aluminium, a lightweight metal with many uses other than motoring. And the turnaround is surprisingly quick – recycled aluminium can be processed into new cans and back on shop shelves within only six weeks.
Considering the growing pressure to curb plastic production and waste, it may be reassuring to know that scrapyards can salvage over 150,000 tonnes of the stuff each year and make it available for use elsewhere, such as sustainable clothing and dog collars.
What to consider when scrapping your car
Unfortunately, scrapping your car isn’t just a case of driving into a scrapyard and handing over the keys. There’s a bit more to think about, but there’s also an opportunity to maximise the money you get for a motor:
- Scrap versus sell – if your car’s still working, it may be more profitable to sell or part exchange with a dealership. This takes away most of the hassle and could leave you with a decent amount to put down as a deposit! To find out how much your car is worth in an instant, use our simple Sell My Car valuation tool.
- Shop about – depending on the parts already at their disposal, some scrapyards may offer more for a particular car if they don’t already have many of those parts. Sites such as Scrap Car Comparison can provide quick quotes.
- Beware of dodgy dealers – if a deal seems too good to be true, it often is. Bear in mind that car scrapping is subject to strict EU and UK laws, and it’s illegal for scrapyards to pay in cash, so those trying to bend the rules should be avoided.
- Remove valuables – this one’s an obvious but important point: make sure to take any valuables from the car before it’s handed over to a scrapyard.
- Sell parts yourself to boost profits – as scrapping is focused on salvaging raw materials, you may be better off selling some components yourself. From stereos to seats, many parts can be reconditioned and fitted to other vehicles, so consider removing these beforehand.
For more features, insight and industry news, give the Bristol Street Motors Newsroom a look, or browse our latest deals if you’re on the look for an upgrade.
___________________________________
Methodology
To calculate the materials retrieved by UK scrapyards, we examined the manufacturing process for the average car and multiplied the quantities involved by the average number of cars scrapped each year, one million.